AP Psychology Flashcards Unit 1 is a comprehensive guide to the fundamental concepts of psychology, providing a solid foundation for students embarking on their journey into the complexities of the human mind. Through engaging and accessible explanations, this unit covers a wide range of topics, from the basic principles of psychology to the biological bases of behavior, sensation and perception, learning, memory, and more.
Prepare to delve into the intricate workings of the nervous system, explore the influence of hormones on behavior, and unravel the mysteries of perception. This unit lays the groundwork for a deeper understanding of human cognition, motivation, emotion, and development, equipping students with a toolkit of essential knowledge for their AP Psychology journey.
Key Concepts
Psychology is the scientific study of the human mind and behavior. It seeks to understand the thoughts, feelings, and actions of individuals and groups.
The basic principles of psychology include:
- The mind and body are interconnected.
- Behavior is influenced by both internal and external factors.
- People are unique and have different ways of thinking, feeling, and behaving.
- Psychology can be used to help people understand themselves and others.
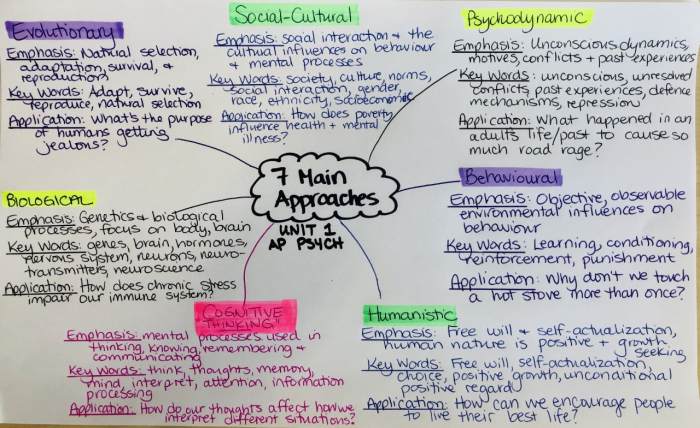
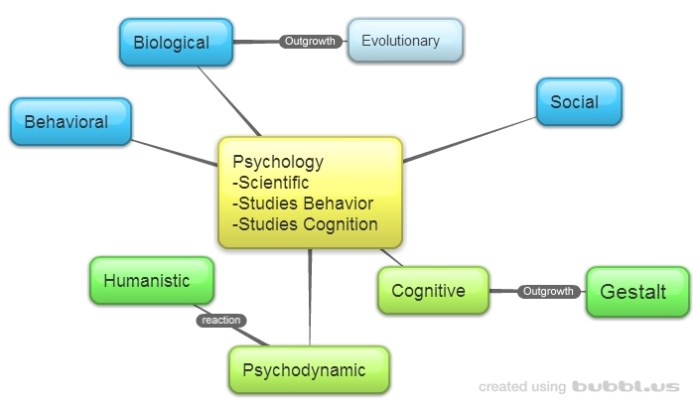
Different Psychological Perspectives
There are many different psychological perspectives, each with its own unique set of assumptions and methods. Some of the most common perspectives include:
- The psychodynamic perspective focuses on the unconscious mind and early childhood experiences.
- The behavioral perspective focuses on observable behavior and the environment.
- The cognitive perspective focuses on mental processes such as thinking, memory, and language.
- The humanistic perspective focuses on the individual’s unique potential and subjective experience.
The Scientific Method in Psychology
The scientific method is a systematic approach to studying behavior and mental processes. It involves:
- Making observations.
- Formulating hypotheses.
- Testing hypotheses.
- Drawing conclusions.
The scientific method is essential for ensuring that psychological research is objective and reliable.
Biological Bases of Behavior
The biological bases of behavior encompass the intricate interplay between our nervous system, hormones, and genetics, which shape our actions, thoughts, and emotions.
Understanding these biological underpinnings is crucial for unraveling the complexities of human behavior and gaining insights into mental health and well-being.
Structure and Function of the Nervous System
The nervous system is the intricate network of specialized cells that orchestrates all bodily functions, including behavior.
- Neurons:The fundamental units of the nervous system, neurons transmit electrical and chemical signals throughout the body.
- Central Nervous System (CNS):Consists of the brain and spinal cord, the CNS processes and interprets information.
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS):Connects the CNS to the rest of the body, transmitting sensory and motor signals.
- Somatic Nervous System:Controls voluntary movements, such as walking and talking.
- Autonomic Nervous System:Regulates involuntary functions, such as heart rate and digestion.
Hormones and Behavior
Hormones are chemical messengers produced by endocrine glands that influence various aspects of behavior.
- Estrogen and Testosterone:Sex hormones that affect sexual behavior, mood, and aggression.
- Cortisol:A stress hormone that prepares the body for “fight or flight” responses.
- Oxytocin:A “love hormone” that promotes bonding, trust, and social behavior.
Genetics and Behavior
Our genetic makeup plays a significant role in shaping our behavior.
- Heritability:The extent to which genes contribute to individual differences in behavior.
- Twin Studies:Compare the similarity of traits between identical and fraternal twins to estimate heritability.
- Genome-Wide Association Studies (GWAS):Identify genetic variants associated with specific behaviors.
Sensation and Perception
Sensation and perception are two intertwined processes that allow us to experience and interpret our surroundings. Sensation refers to the initial detection of physical stimuli by our sensory receptors, while perception is the process of organizing and interpreting these sensory inputs to form a meaningful representation of the world.
Types of Sensory Receptors
Our bodies are equipped with specialized sensory receptors that respond to different types of stimuli. These receptors can be classified into two main categories:
- Exteroceptors: Detect stimuli from the external environment, such as touch, temperature, pain, and light.
- Interoceptors: Detect stimuli from within the body, such as hunger, thirst, and pain.
Role of Attention in Perception
Perception is not a passive process; it is actively influenced by our attention. Attention allows us to focus on specific stimuli and ignore others, which helps us to prioritize and process information effectively.
- Selective attention: The ability to focus on a specific stimulus or set of stimuli while ignoring others.
- Divided attention: The ability to attend to multiple stimuli simultaneously.
Learning
Learning refers to a relatively permanent change in behavior or mental processes that occurs as a result of experience. It involves acquiring new knowledge, skills, or behaviors, and can be either conscious or unconscious.
Types of Learning
There are several different types of learning, each with its own characteristics and processes:
- Classical Conditioning:Involves associating a neutral stimulus with a meaningful stimulus, leading to a conditioned response.
- Operant Conditioning:Involves reinforcing or punishing behaviors to increase or decrease their frequency.
- Social Learning:Involves learning through observing and imitating others.
- Cognitive Learning:Involves actively processing and organizing information to acquire new knowledge and skills.
Factors Influencing Learning
Several factors can influence the effectiveness of learning, including:
- Motivation:Intrinsic or extrinsic factors that drive an individual to learn.
- Attention:The ability to focus and concentrate on the learning material.
- Memory:The ability to encode, store, and retrieve information.
- Feedback:Information provided about the correctness or effectiveness of a response.
- Transfer:The ability to apply learned knowledge or skills to new situations.
Applications of Learning Principles
The principles of learning have wide applications in various fields, including:
- Education:Designing effective teaching methods and curricula.
- Training and Development:Developing and implementing training programs.
- Behavior Modification:Modifying problematic behaviors through techniques like operant conditioning.
- Advertising:Using principles of classical conditioning to create effective advertisements.
- Personal Growth:Applying learning principles to enhance personal development and well-being.
Memory
Memory is the ability to encode, store, and retrieve information. It allows us to learn from our experiences, remember important events, and make plans for the future. There are many different types of memory, each with its own unique characteristics.
AP Psychology flashcards unit 1 is a valuable resource for students preparing for the exam. However, if you’re also studying for the real estate express final exam , you may find that the content overlaps. By cross-referencing the two sets of flashcards, you can reinforce your understanding of key concepts and improve your performance on both exams.
Types of Memory
The three main types of memory are:
- Sensory memory: Stores sensory information for a very brief period of time, usually less than a second.
- Short-term memory: Stores information for a few seconds or minutes, and can be accessed consciously.
- Long-term memory: Stores information for an indefinite period of time, and can be accessed consciously or unconsciously.
Processes of Memory
Memory involves three main processes:
- Encoding: The process of converting information into a form that can be stored in memory.
- Storage: The process of maintaining information in memory over time.
- Retrieval: The process of accessing information from memory.
Factors that Influence Memory
Many factors can influence memory, including:
- Attention: Paying attention to information helps to encode it into memory.
- Rehearsal: Repeating information helps to strengthen the memory trace.
- Organization: Organizing information into meaningful chunks makes it easier to remember.
- Emotion: Emotional events are more likely to be remembered than neutral events.
- Sleep: Sleep helps to consolidate memories.
Thinking and Language
Thinking is the cognitive process of using our knowledge and mental abilities to understand the world around us. It involves processes such as reasoning, problem-solving, decision-making, and creativity. Thinking is influenced by our perceptions, memories, emotions, and experiences. Language plays a crucial role in thinking, as it allows us to represent our thoughts, communicate with others, and organize information.
Types of Thinking
There are different types of thinking, including:
-
-*Inductive reasoning
Drawing general conclusions from specific observations.
-*Deductive reasoning
Making specific predictions from general principles.
-*Abstract thinking
Using symbols and concepts to represent ideas and relationships.
-*Critical thinking
Evaluating information and arguments to make sound judgments.
-*Creative thinking
Generating new ideas and solutions.
Language and Thinking
Language is closely intertwined with thinking. It provides us with the symbols and structures necessary to represent our thoughts. Language allows us to communicate our ideas, share knowledge, and collaborate with others. The relationship between language and thinking is bidirectional, as language both shapes and is shaped by our thoughts.
Thinking and Problem-Solving
Thinking plays a central role in problem-solving. When faced with a problem, we use our thinking abilities to analyze the situation, identify potential solutions, and evaluate their feasibility. Problem-solving often involves trial and error, as well as the application of logical reasoning and creative thinking.
Motivation and Emotion
Motivation and emotion are closely intertwined psychological processes that drive our thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. Motivation refers to the internal forces that drive us to act, while emotion refers to the subjective experiences that accompany these actions.
Motivation can be classified into two main types: intrinsic motivation and extrinsic motivation. Intrinsic motivation arises from within an individual and is driven by a desire to engage in an activity for its own sake, such as enjoying a hobby or pursuing a personal goal.
Extrinsic motivation, on the other hand, arises from external sources and is driven by rewards or punishments, such as working for a paycheck or avoiding a fine.
Factors that influence motivation include biological needs, social and environmental factors, and cognitive processes. Biological needs, such as hunger and thirst, drive us to seek out food and water. Social and environmental factors, such as rewards and punishments, can also influence our motivation.
Cognitive processes, such as setting goals and expectations, can also affect our motivation.
Motivation and emotion are closely related. Emotions can influence our motivation, and motivation can influence our emotions. For example, feeling happy or excited can motivate us to pursue a goal, while feeling sad or angry can discourage us from pursuing a goal.
Intrinsic Motivation
- Definition: Intrinsic motivation is the desire to engage in an activity for its own sake, without external rewards or punishments.
- Examples: Pursuing a hobby, playing a sport for enjoyment, or volunteering.
- Benefits: Intrinsic motivation is associated with higher levels of engagement, creativity, and satisfaction.
Development: Ap Psychology Flashcards Unit 1
Human development is a fascinating process that begins at conception and continues throughout our lives. It involves significant changes in our physical, cognitive, and emotional abilities, as well as our social and behavioral patterns.
Developmental psychology is the scientific study of these changes and the factors that influence them. It provides insights into how we grow and change from infancy to adolescence, adulthood, and old age.
Stages of Human Development
Human development can be divided into several distinct stages, each with its unique characteristics:
- Prenatal Stage(conception to birth): Involves the growth and development of the fetus within the mother’s womb.
- Infancy(birth to 18 months): Characterized by rapid physical growth and cognitive development, including the development of language and motor skills.
- Toddlerhood(18 months to 3 years): A period of increased independence and exploration, as toddlers begin to walk, talk, and interact more with their surroundings.
- Preschool(3 to 6 years): A time of significant cognitive and social development, as children begin to engage in imaginative play, learn basic concepts, and develop friendships.
- Middle Childhood(6 to 11 years): A period of further cognitive and social development, as children become more independent and begin to develop their own interests and values.
- Adolescence(11 to 18 years): A time of significant physical, cognitive, and emotional changes, as teenagers navigate the transition from childhood to adulthood.
- Young Adulthood(18 to 25 years): A period of emerging adulthood, as individuals explore their independence, establish their careers, and form intimate relationships.
- Adulthood(25 to 65 years): A time of stability and productivity, as individuals continue to develop their careers, families, and social networks.
- Late Adulthood(65+ years): A period of physical and cognitive decline, as individuals adjust to retirement and navigate the challenges of aging.
Factors Influencing Development
Human development is influenced by a complex interplay of biological, environmental, and social factors:
- Biological Factors: Genes, hormones, and other biological processes play a crucial role in shaping our physical and cognitive development.
- Environmental Factors: The environment in which we grow up, including our family, school, and community, has a profound impact on our development.
- Social Factors: Our interactions with others, including our parents, siblings, peers, and teachers, shape our social and emotional development.
Applications of Developmental Psychology
Developmental psychology has numerous applications in the real world, including:
- Education: Understanding developmental stages and factors that influence learning can help educators create effective teaching strategies.
- Parenting: Knowledge of developmental milestones and challenges can help parents provide appropriate support and guidance to their children.
- Mental Health: Developmental psychology can help clinicians identify and treat developmental disorders and mental health issues.
- Social Policy: Understanding developmental processes can inform social policies that support healthy child development.
Personality
Personality refers to the unique and enduring characteristics that shape an individual’s thoughts, feelings, and behaviors. It encompasses a complex interplay of biological, psychological, and environmental factors that influence how we perceive ourselves, others, and the world around us.
Theories of Personality
- Psychodynamic Theory:Focuses on unconscious conflicts and childhood experiences as the primary determinants of personality. Key concepts include the id, ego, and superego.
- Behaviorism:Emphasizes the role of learning and environmental conditioning in shaping personality. Behaviors are reinforced or punished, leading to the development of specific personality traits.
- Humanistic Theory:Views personality as a product of free will and self-actualization. Individuals are seen as capable of growth and personal fulfillment through their own choices and experiences.
- Trait Theory:Proposes that personality is composed of stable and measurable traits, such as extroversion, agreeableness, and conscientiousness. These traits influence how individuals respond to situations and interact with others.
- Social Cognitive Theory:Emphasizes the interaction between cognitive processes, environmental factors, and personal experiences in shaping personality. Individuals learn and adapt their behaviors based on their perceptions and beliefs.
Factors Influencing Personality
- Genetics:Inherited traits play a role in shaping personality characteristics, such as temperament and emotional reactivity.
- Environment:Childhood experiences, cultural influences, and social interactions significantly impact personality development.
- Cognitive Processes:Thought patterns, beliefs, and perceptions influence how individuals interpret and respond to their environment.
- Emotion:Emotional experiences and the ability to regulate emotions contribute to the development of personality traits.
- Life Experiences:Major life events, such as trauma, loss, or significant achievements, can shape personality characteristics.
Applications of Personality Psychology, Ap psychology flashcards unit 1
Personality psychology has practical applications in various fields, including:
- Clinical Psychology:Understanding personality disorders and developing treatment plans.
- Organizational Psychology:Selecting and managing employees, predicting job performance.
- Forensic Psychology:Profiling criminals and assessing risk factors for recidivism.
- Health Psychology:Promoting healthy behaviors and coping mechanisms.
- Education:Designing personalized learning experiences and understanding individual learning styles.
Social Psychology

Social psychology investigates the influence of social factors on individual and group behavior, cognition, and emotion. It examines how people’s thoughts, feelings, and actions are shaped by their social environment, including interactions with others, social norms, and cultural influences.
Principles of Social Psychology
- Social influence:People’s behavior is influenced by the actions, opinions, and expectations of others.
- Social cognition:People process and interpret social information, such as the behavior of others, to make sense of their social world.
- Social identity:People define themselves in terms of their social groups and adopt the norms and values of those groups.
- Group dynamics:Groups influence individual behavior through norms, roles, and social hierarchies.
Factors Influencing Social Behavior
- Culture:Cultural norms, values, and beliefs shape social behavior.
- Social norms:Unwritten rules that govern behavior in a society.
- Social roles:Expectations associated with specific positions in society.
- Socialization:The process by which individuals learn social norms and values.
Applications of Social Psychology
Social psychology is applied in various fields, including:
- Marketing and advertising:Understanding social influence to design effective campaigns.
- Education:Promoting positive social interactions and reducing bullying.
- Health promotion:Encouraging healthy behaviors by leveraging social norms and group dynamics.
- Conflict resolution:Facilitating communication and understanding between conflicting parties.
Clinical Psychology
Clinical psychology focuses on the assessment, diagnosis, and treatment of mental disorders. Mental disorders are characterized by significant disturbances in thinking, emotion, or behavior that cause distress or impairment in functioning.
There are many different types of mental disorders, including anxiety disorders, mood disorders, psychotic disorders, and personality disorders. The specific symptoms of a mental disorder can vary depending on the individual and the type of disorder.
Factors Contributing to Mental Disorders
The factors that contribute to mental disorders are complex and can include:
- Genetics: Some mental disorders are thought to be caused by genetic factors.
- Brain chemistry: Imbalances in brain chemistry can contribute to mental disorders.
- Life experiences: Traumatic or stressful life events can trigger mental disorders.
- Environmental factors: Exposure to toxins or other environmental factors can increase the risk of developing a mental disorder.
Treatments for Mental Disorders
There are a variety of treatments for mental disorders, including:
- Psychotherapy: Psychotherapy involves talking to a mental health professional about your thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
- Medication: Medication can be used to treat symptoms of mental disorders such as anxiety, depression, and psychosis.
- Lifestyle changes: Making healthy lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and getting enough sleep, can help to improve mental health.
- Support groups: Support groups can provide a sense of community and support for people with mental disorders.
FAQ Section
What is the scientific method as applied to psychology?
The scientific method involves observing a phenomenon, forming a hypothesis, testing the hypothesis through experimentation, analyzing the results, and drawing conclusions.
How do hormones influence behavior?
Hormones are chemical messengers that regulate various bodily functions, including mood, aggression, and reproductive behavior.
What are the different types of learning?
There are various types of learning, including classical conditioning, operant conditioning, and social learning.