Mrp works best if the inventory items have dependent demand. – MRP (Material Requirements Planning) is an inventory management technique that excels when inventory items exhibit dependent demand. This dependency, where the demand for one item is contingent on the demand for another, significantly impacts MRP’s effectiveness.
Understanding this relationship is crucial for optimizing inventory accuracy, reducing lead times, and maximizing the benefits of MRP.
MRP’s Dependency on Inventory Items
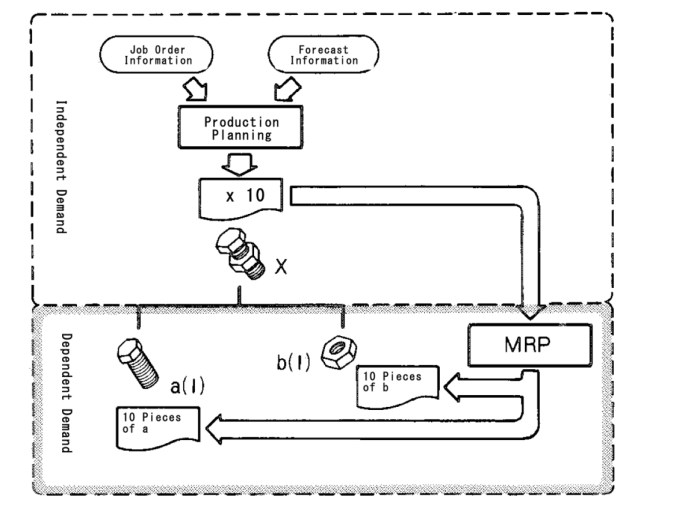
Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is a production planning and inventory control system that calculates the materials and components needed to produce a finished product. MRP’s effectiveness depends on the accuracy of its data, including the demand for inventory items.
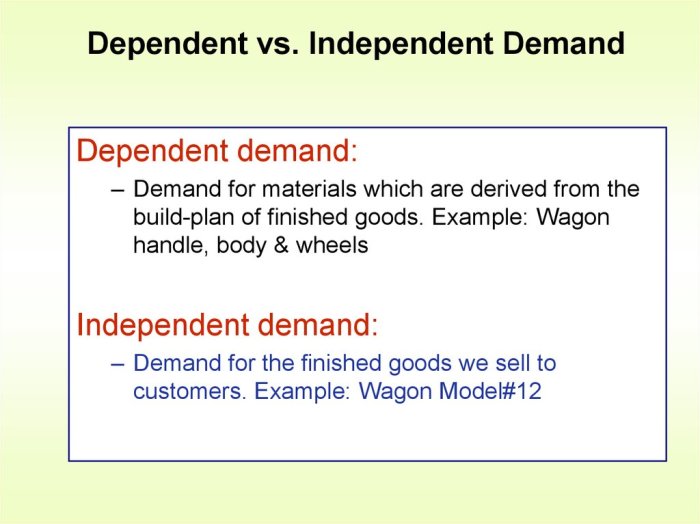
Dependent demand refers to the situation where the demand for one inventory item is directly related to the demand for another inventory item. For example, the demand for tires is dependent on the demand for cars.
MRP works best if the inventory items have dependent demand. This is because MRP can use the demand for the finished product to calculate the demand for the components needed to produce it.
Benefits of MRP for Items with Dependent Demand
- Improved inventory accuracy: MRP can help to ensure that the right inventory items are available at the right time. This can reduce the risk of stockouts and overstocking.
- Reduced lead times: MRP can help to reduce lead times by identifying the components that need to be ordered in advance. This can help to ensure that production is not delayed.
- Increased customer satisfaction: MRP can help to improve customer satisfaction by ensuring that the products they want are available when they need them.
Challenges of MRP for Items with Dependent Demand
- Demand variability: The demand for inventory items with dependent demand can be highly variable. This can make it difficult to forecast demand accurately.
- Forecasting accuracy: The accuracy of MRP’s calculations depends on the accuracy of its demand forecasts. If the forecasts are inaccurate, MRP may not be able to generate accurate production plans.
Best Practices for MRP with Dependent Demand
- Use accurate demand forecasts: The accuracy of MRP’s calculations depends on the accuracy of its demand forecasts. Therefore, it is important to use accurate forecasting methods and to regularly update the forecasts.
- Use a rolling planning horizon: MRP should be used with a rolling planning horizon. This means that the plan is updated regularly to reflect the latest demand forecasts.
- Use safety stock: Safety stock is a buffer of inventory that is kept on hand to protect against unexpected increases in demand. Safety stock can help to reduce the risk of stockouts.
Comparison of MRP with Other Inventory Management Techniques, Mrp works best if the inventory items have dependent demand.
| MRP | JIT | Kanban | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Focus | Production planning | Inventory reduction | Just-in-time production |
| Advantages | Improved inventory accuracy, reduced lead times, increased customer satisfaction | Reduced inventory levels, improved cash flow | Reduced waste, improved flexibility |
| Disadvantages | Can be complex and time-consuming to implement, requires accurate demand forecasts | Can lead to stockouts if demand is not accurately forecasted | Can be difficult to implement in complex production environments |
Query Resolution: Mrp Works Best If The Inventory Items Have Dependent Demand.
What is dependent demand in inventory management?
Dependent demand refers to the situation where the demand for an inventory item is directly influenced by the demand for another item.
How does MRP benefit inventory items with dependent demand?
MRP helps manage inventory items with dependent demand by accurately forecasting demand, optimizing inventory levels, and ensuring timely availability of components.
What are the challenges of using MRP for items with dependent demand?
Challenges include demand variability, forecasting accuracy, and managing the complexity of dependent relationships.