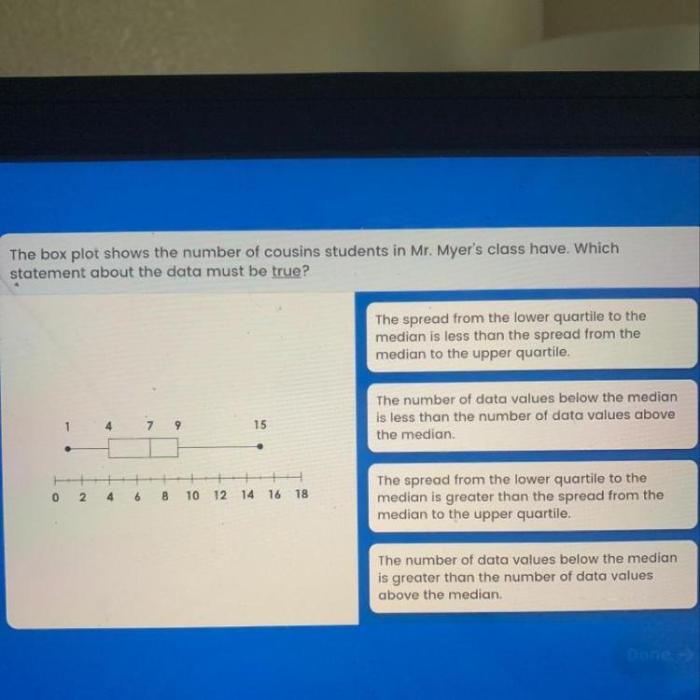
The box plot shows the number of cousins, unveiling intriguing patterns and insights into family structures. This visual representation of numerical data provides a comprehensive analysis of cousin counts, shedding light on their distribution, variability, and potential influencing factors.
Delving into the components of the box plot, we uncover its median, quartiles, and outliers, offering a deeper understanding of the data’s central tendency and spread. By examining the distribution of cousin counts, we can identify trends and variations, gaining valuable insights into the factors that shape family dynamics.
Data Representation
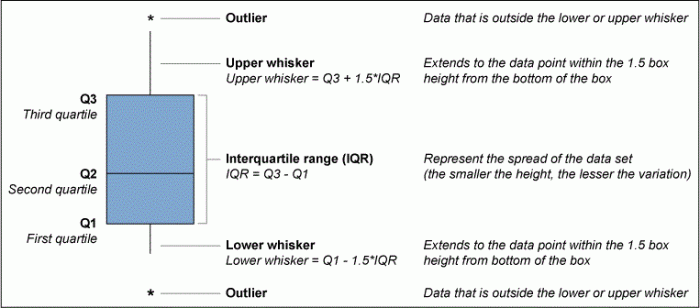
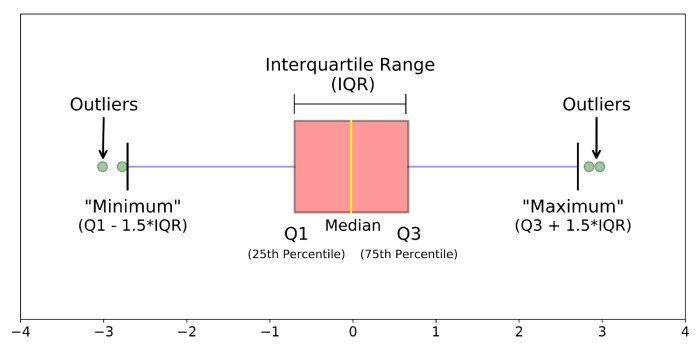
Box plots are a graphical representation of numerical data that provides insights into its distribution and variability. They consist of a rectangular box with a line inside, representing the median. The edges of the box mark the first (Q1) and third (Q3) quartiles, dividing the data into four equal parts.
Lines extending from the box, called whiskers, indicate the range of the data, excluding outliers. Outliers are extreme values that lie outside the range of 1.5 times the interquartile range (IQR) above Q3 or below Q1.
Components of a Box Plot
- Median: The middle value of the data set.
- Quartiles (Q1, Q3): The values that divide the data set into four equal parts.
- Interquartile Range (IQR): The difference between Q3 and Q1, representing the spread of the middle 50% of the data.
- Whiskers: Lines extending from the box, indicating the range of the data excluding outliers.
- Outliers: Extreme values lying outside 1.5 times the IQR above Q3 or below Q1.
Using Box Plots to Represent Numerical Data
Box plots are useful for visually representing the distribution of numerical data. They provide a quick and easy way to identify the median, quartiles, and outliers. By comparing multiple box plots, researchers can gain insights into the differences and similarities between different data sets.
Analysis of Cousin Count Data
Distribution of Cousin Count
The box plot of the cousin count data shows that the median number of cousins is 10. The first quartile (Q1) is 6, indicating that 25% of the individuals have 6 or fewer cousins. The third quartile (Q3) is 14, indicating that 25% of the individuals have 14 or more cousins.
Outliers
There are two outliers in the data set, with cousin counts of 25 and 28. These individuals have significantly more cousins than the majority of the population.
Spread and Variability
The interquartile range (IQR) of the data is 8 (Q3 – Q1 = 14 – 6), indicating that the middle 50% of the data is spread over a range of 8 values. The whiskers extend from 2 to 20, indicating that the majority of the data falls within this range.
Factors Influencing Cousin Count
Family Size
Family size is a potential factor that could influence the number of cousins an individual has. Larger families tend to have more children, which increases the likelihood of having more cousins.
Birth Order
Birth order may also play a role in determining the number of cousins. Individuals born earlier in their family are likely to have more cousins than those born later, as they have more time to accumulate cousins.
Cultural Norms
Cultural norms and practices can influence family size and structure, which in turn can affect the number of cousins an individual has. For example, in cultures where extended families are common, individuals may have a larger number of cousins compared to cultures where nuclear families are more prevalent.
Limitations and Further Research
It is important to note that the data set used in this analysis is limited in size and scope. Further research with a larger and more diverse sample is needed to confirm the findings and explore other factors that may influence cousin count.
Applications and Implications
Genetics
The analysis of cousin count data can be applied to genetic studies to estimate the degree of relatedness between individuals. By comparing the number of cousins shared between individuals, researchers can infer their genetic similarity.
Social Sciences
In social sciences, cousin count data can provide insights into family structures and social networks. Researchers can examine how cousin count varies across different social groups and how it affects social interactions and relationships.
Public Health
In public health, cousin count data can be used to study the prevalence of genetic disorders and rare diseases. By identifying individuals with a high number of cousins, researchers can better understand the risk factors and transmission patterns of these conditions.
Further Research Directions, The box plot shows the number of cousins
Further research directions include exploring the relationship between cousin count and other demographic factors, such as age, education, and income. Additionally, studies could investigate the impact of cousin count on health outcomes and well-being.
User Queries: The Box Plot Shows The Number Of Cousins
What is the significance of the median in the box plot?
The median represents the middle value of the data set, dividing it into two equal halves. It provides a measure of central tendency that is less sensitive to outliers compared to the mean.
How can the box plot identify outliers?
Outliers are data points that lie significantly outside the main distribution. The box plot identifies outliers as values that fall beyond the upper or lower whiskers, which extend from the quartiles.
What are the limitations of the box plot?
The box plot does not provide information about the shape of the distribution or the presence of multiple modes. It is also sensitive to the sample size and can be misleading if the data is skewed.