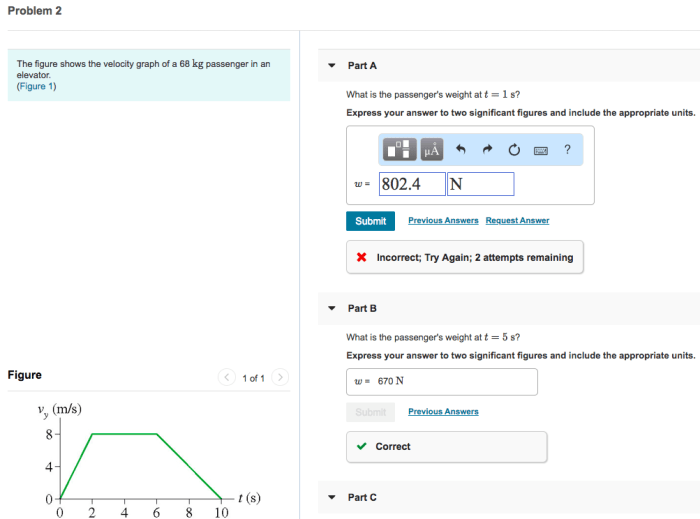
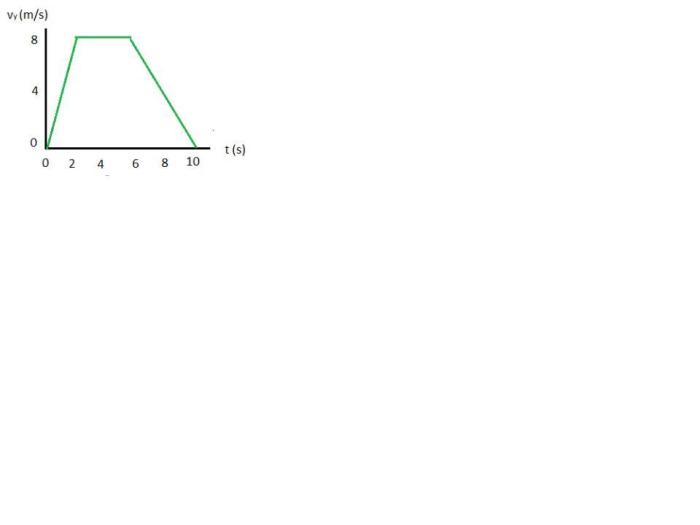
What is the passenger’s apparent weight at t 1.0 s – What is the passenger’s apparent weight at t = 1.0 s? This question delves into the fascinating realm of apparent weight, a concept that plays a crucial role in elevator design and passenger safety. As we embark on this journey, we will unravel the factors that influence apparent weight, explore its safety implications, and uncover its practical applications in elevator engineering.
Apparent weight, distinct from true weight, is the force exerted by a surface on an object due to gravity and any other accelerations acting upon it. This concept becomes particularly relevant in elevators, where passengers experience varying apparent weights as the elevator accelerates, decelerates, or changes direction.
What is the Passenger’s Apparent Weight at t = 1.0 s?
The apparent weight of a passenger in an elevator is the force exerted on the passenger by the elevator floor. It differs from the true weight of the passenger, which is the force exerted on the passenger by the Earth’s gravitational field.
The apparent weight of a passenger in an elevator can be calculated using the following equation:
Wa= m(g
a)
where:
- W ais the apparent weight of the passenger (in newtons)
- m is the mass of the passenger (in kilograms)
- g is the acceleration due to gravity (9.8 m/s 2)
- a is the acceleration of the elevator (in m/s 2)
Factors Affecting Apparent Weight, What is the passenger’s apparent weight at t 1.0 s
The apparent weight of a passenger in an elevator at t = 1.0 s is affected by the following factors:
- Speed of the elevator:The speed of the elevator does not affect the apparent weight of the passenger.
- Acceleration of the elevator:The acceleration of the elevator affects the apparent weight of the passenger. If the elevator is accelerating upward, the apparent weight of the passenger will be greater than their true weight. If the elevator is accelerating downward, the apparent weight of the passenger will be less than their true weight.
- Direction of the elevator’s motion:The direction of the elevator’s motion affects the apparent weight of the passenger. If the elevator is moving upward, the apparent weight of the passenger will be greater than their true weight. If the elevator is moving downward, the apparent weight of the passenger will be less than their true weight.
Calculating Apparent Weight at t = 1.0 s
To calculate the apparent weight of a passenger in an elevator at t = 1.0 s, follow these steps:
- Determine the mass of the passenger (in kilograms).
- Determine the acceleration of the elevator (in m/s2).
- Substitute the values for mass and acceleration into the equation for apparent weight: W a= m(g
a).
- Calculate the apparent weight of the passenger (in newtons).
Example:A passenger with a mass of 70 kg is in an elevator that is accelerating upward at a rate of 2 m/s 2. What is the passenger’s apparent weight at t = 1.0 s?
W a= m(g – a) = 70 kg(9.8 m/s 2– 2 m/s 2) = 548 N
Therefore, the passenger’s apparent weight at t = 1.0 s is 548 N.
Safety Implications
Excessive apparent weight changes can cause discomfort, injury, or even fainting. This is because the human body is not designed to withstand large changes in apparent weight. When the apparent weight of a passenger changes suddenly, the body’s circulatory system can be overwhelmed, which can lead to dizziness, nausea, and fainting.
To prevent excessive apparent weight changes, elevators are designed with safety features such as speed limits and emergency braking systems. These features help to ensure that the apparent weight of passengers does not change too quickly.
Applications
Understanding apparent weight is important for the design and operation of elevators. By considering the factors that affect apparent weight, elevator designers can create elevators that are safe and comfortable for passengers.
Apparent weight considerations can also influence elevator safety features, such as speed limits and emergency braking systems. By understanding the effects of apparent weight on passengers, elevator designers can create elevators that are safe and reliable.
FAQ Compilation: What Is The Passenger’s Apparent Weight At T 1.0 S
What is the difference between apparent weight and true weight?
Apparent weight is the force exerted by a surface on an object due to gravity and any other accelerations acting upon it, while true weight is the force exerted by gravity alone.
How does elevator acceleration affect passenger apparent weight?
Elevator acceleration causes changes in passenger apparent weight. During upward acceleration, apparent weight increases, while during downward acceleration, it decreases.
Why is it important to consider apparent weight in elevator design?
Considering apparent weight in elevator design helps ensure passenger safety and comfort. Excessive apparent weight changes can cause discomfort, injury, or fainting.