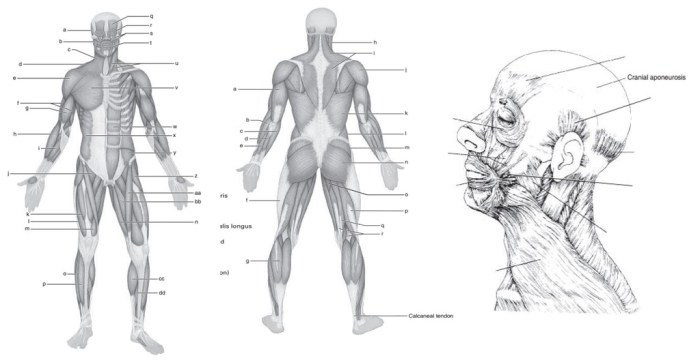
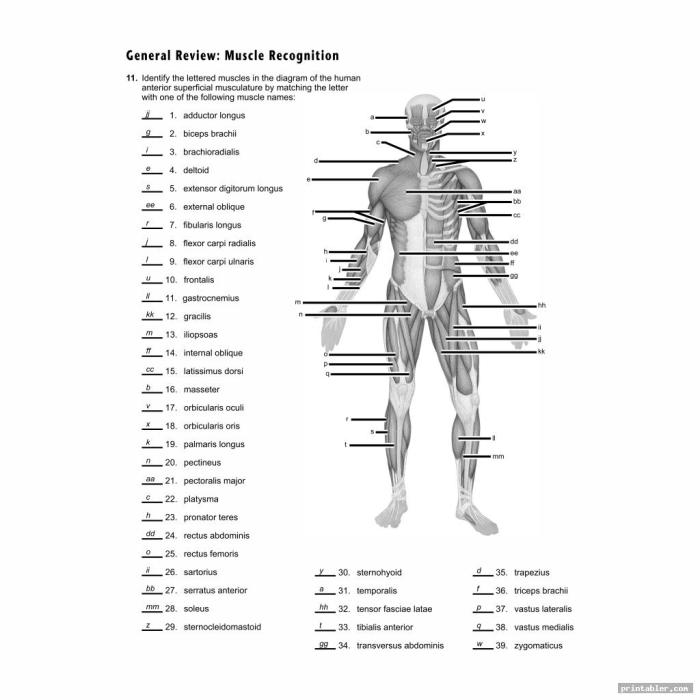
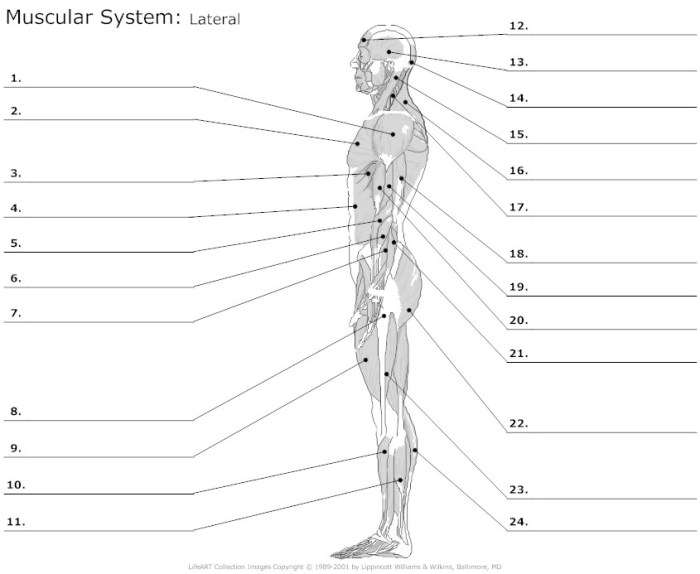
Delving into the Muscular System Worksheet Answer Key, we embark on an enlightening journey to unravel the complexities of our muscular system. This comprehensive guide unveils the intricate workings of muscles, empowering you with a profound understanding of their structure, function, and significance.
From the fundamental components of muscle tissue to the dynamic process of muscle contraction, we meticulously explore the fascinating realm of human movement. Discover the essential roles played by tendons and ligaments, delve into the mechanisms of muscle disorders, and witness the transformative effects of exercise on our muscular system.
Muscular System
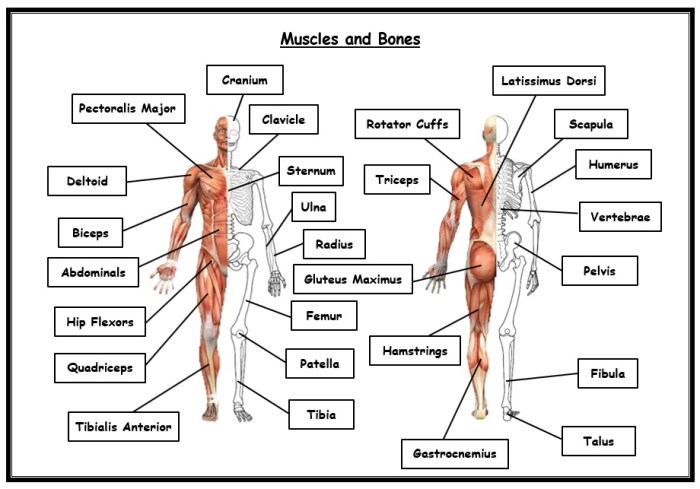
The muscular system is a complex and intricate network of tissues that work together to produce movement, maintain posture, and generate heat. Muscles are made up of specialized cells that can contract and relax, allowing for a wide range of movements, from the delicate movements of the fingers to the powerful contractions of the legs.
1. Muscular System Components, Muscular system worksheet answer key
The muscular system consists of three main types of muscle tissues: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Skeletal muscle is attached to bones and is responsible for voluntary movements, such as walking, running, and lifting objects. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of organs and blood vessels and is responsible for involuntary movements, such as digestion and blood flow regulation.
Cardiac muscle is found only in the heart and is responsible for the rhythmic contractions that pump blood throughout the body.Muscles are composed of bundles of muscle fibers, which are long, cylindrical cells that contain specialized proteins called actin and myosin.
When these proteins interact, they cause the muscle fibers to contract, which in turn causes the muscle to shorten.Tendons are tough, fibrous cords of connective tissue that attach muscles to bones. Ligaments are similar to tendons, but they connect bones to bones.
Both tendons and ligaments help to stabilize joints and prevent them from dislocating.
2. Muscle Contraction
Muscle contraction is a complex process that involves the interaction of actin and myosin proteins. When a muscle is stimulated by a nerve impulse, calcium ions are released into the muscle fiber. These calcium ions bind to receptors on the surface of the actin filaments, causing them to change shape.
This change in shape allows the myosin filaments to bind to the actin filaments and pull them toward the center of the muscle fiber. This process, known as the sliding filament mechanism, causes the muscle fiber to shorten and the muscle to contract.The
energy for muscle contraction comes from a molecule called adenosine triphosphate (ATP). ATP is broken down into adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and inorganic phosphate (Pi), releasing energy that is used to power the sliding filament mechanism.
3. Muscle Groups
The major muscle groups of the body can be organized into four columns:| Muscle Group | Description | Function ||—|—|—||*Upper Body |
-*Pectorals
Chest | Flexion and adduction of the arm |
| |
-*Biceps
Front of the upper arm | Flexion of the elbow || |
-*Triceps
Back of the upper arm | Extension of the elbow || |
-*Deltoids
Shoulders | Abduction, flexion, and extension of the arm || |
-*Trapezius
Back of the neck and shoulders | Elevation and retraction of the scapulae || |
-*Rhomboids
Back of the shoulders | Retraction and elevation of the scapulae || |
-*Latissimus dorsi
Back | Extension, adduction, and rotation of the arm ||*Lower Body |
-*Quadriceps
Front of the thigh | Extension of the knee |
| |
-*Hamstrings
Back of the thigh | Flexion of the knee || |
-*Calves
Back of the lower leg | Plantar flexion of the foot || |
-*Gluteals
Buttocks | Extension, abduction, and rotation of the hip || |
-*Hamstrings
Back of the thigh | Flexion of the knee || |
-*Adductors
Inner thigh | Adduction of the thigh || |
-*Abductors
Outer thigh | Abduction of the thigh ||*Core |
-*Abdominals
Front of the abdomen | Flexion and rotation of the trunk |
| |
-*Obliques
Sides of the abdomen | Flexion and rotation of the trunk || |
-*Erector spinae
Back | Extension of the trunk || |
-*Multifidus
Back | Rotation and stabilization of the trunk ||*Other |
-*Facial muscles
Face | Facial expressions |
| |
-*Ocular muscles
Eyes | Movement of the eyes || |
-*Tongue muscles
Tongue | Speech and swallowing |
4. Muscle Disorders
There are a number of muscle disorders that can affect people of all ages. Some of the most common muscle disorders include:*
-*Muscular dystrophy
A group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle weakness and degeneration.
-
-*Myasthenia gravis
An autoimmune disorder that causes muscle weakness and fatigue.
-*Fibromyalgia
A chronic condition that causes widespread muscle pain and fatigue.
The symptoms of muscle disorders can vary depending on the specific disorder. Some common symptoms include:* Muscle weakness
- Muscle pain
- Muscle fatigue
- Stiffness
- Cramps
- Twitching
The causes of muscle disorders can also vary depending on the specific disorder. Some muscle disorders are caused by genetic mutations, while others are caused by autoimmune disorders or other factors.There is no cure for most muscle disorders, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms.
These treatments may include:* Physical therapy
- Occupational therapy
- Medication
- Surgery
There are also a number of things that people can do to help prevent muscle disorders, such as:* Exercising regularly
- Eating a healthy diet
- Getting enough sleep
- Managing stress
5. Muscular System and Exercise
Exercise is essential for maintaining a healthy muscular system. Exercise helps to build muscle strength, power, and endurance. It also helps to improve flexibility and range of motion.There are many different types of exercises that can be beneficial for the muscular system.
Some of the most effective exercises include:*
-*Strength training
Exercises that involve lifting weights or using resistance bands to build muscle strength.
-
-*Cardiovascular exercise
Exercises that get the heart rate up, such as running, swimming, and biking.
-*Flexibility exercises
Exercises that stretch the muscles and improve range of motion.
It is important to warm up before exercising and cool down afterward. Warming up helps to prepare the muscles for exercise and reduce the risk of injury. Cooling down helps to reduce muscle soreness and stiffness.A sample exercise routine that targets different muscle groups is provided below:Monday:
Chest
Bench press, dumbbell flyes
Triceps
Triceps extensions, overhead triceps extensions
Biceps
Bicep curls, hammer curlsTuesday:
Back
Lat pulldowns, rows
Shoulders
Overhead press, lateral raises
Traps
ShrugsWednesday:
Rest
Thursday:
Legs
Squats, leg press
Hamstrings
Hamstring curls, leg curls
Calves
Calf raisesFriday:
Glutes
Glute bridges, hip thrusts
Abs
Crunches, planks
Obliques
Russian twistsSaturday:
Rest
Sunday:
Active recovery
Go for a walk, swim, or bike ride
FAQ Section: Muscular System Worksheet Answer Key
What are the three types of muscle tissues?
Skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle
What is the role of calcium ions in muscle contraction?
Calcium ions trigger the release of ATP, which provides the energy for muscle contraction
What are the symptoms of muscular dystrophy?
Progressive muscle weakness, wasting, and difficulty moving
How can exercise benefit the muscular system?
Exercise strengthens muscles, improves flexibility, and enhances overall physical performance