Exploring the realm of partes del carro en inglés y español unveils a captivating tapestry of automotive engineering, where each component plays a pivotal role in the seamless functioning of a vehicle. Delving into this topic, we embark on a journey to decipher the intricacies of car parts, their functions, and their indispensable contribution to the overall performance and safety of a motor vehicle.
From the exterior panels that define a car’s aesthetic appeal to the intricate inner workings of the engine, transmission, suspension, and braking systems, we delve into the technicalities that govern the operation of modern automobiles. Join us as we navigate the complexities of automotive components, unraveling their significance and appreciating the symphony of engineering that brings a car to life.
Partes Externas del Carro
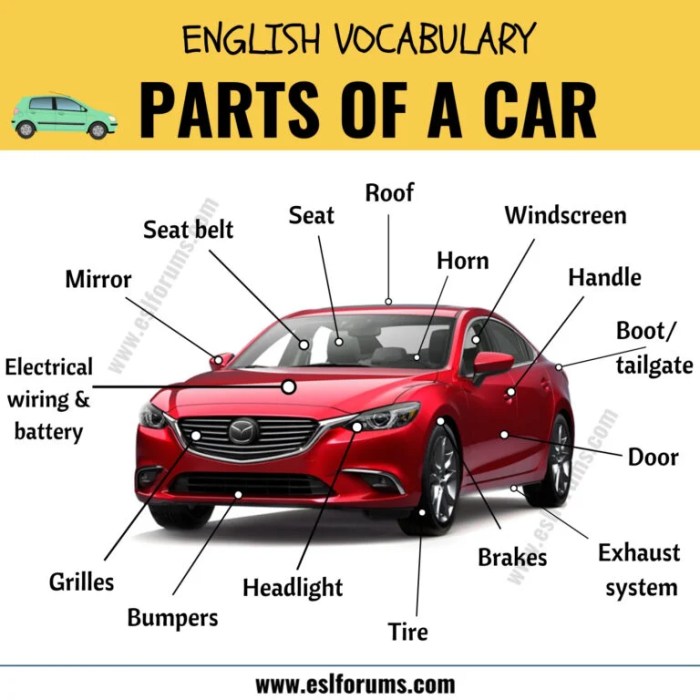
The external parts of a car are the components that are visible from the outside. These parts play a crucial role in the overall functionality, safety, and aesthetics of the vehicle.
The following table provides a comprehensive overview of the external parts of a car, along with their functions and importance:
| Part | Image | Function | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Body | [Image of a car body] | Protects the occupants and internal components from the elements and external impacts. | Ensures the safety and integrity of the vehicle. |
| Windows | [Image of car windows] | Allow visibility for the driver and passengers, and provide ventilation. | Crucial for safe driving and maintaining a comfortable cabin environment. |
| Doors | [Image of car doors] | Provide access to the interior of the vehicle. | Essential for entering and exiting the car, and for loading and unloading cargo. |
| Hood | [Image of a car hood] | Covers the engine compartment and allows access for maintenance and repairs. | Protects the engine and other components from dirt, debris, and moisture. |
| Trunk | [Image of a car trunk] | Provides storage space for luggage and other items. | Convenient for carrying additional items or cargo. |
| Bumpers | [Image of car bumpers] | Absorb impact in low-speed collisions and protect the body from damage. | Enhances safety and reduces repair costs in minor accidents. |
| Headlights | [Image of car headlights] | Provide illumination for nighttime driving and enhance visibility. | Critical for safe driving in low-light conditions. |
| Taillights | [Image of car taillights] | Signal braking and turning intentions to other vehicles. | Ensures safe communication and prevents rear-end collisions. |
| Mirrors | [Image of car mirrors] | Provide the driver with a view of the surroundings and blind spots. | Essential for safe driving and maneuvering. |
| Wheels | [Image of car wheels] | Support the vehicle and allow it to move. | Crucial for mobility and handling. |
| Tires | [Image of car tires] | Provide traction, absorb shock, and protect the wheels from damage. | Essential for safe and comfortable driving. |
Partes Internas del Motor
The internal parts of a car engine are the components that make up the engine’s core and are responsible for its operation. These parts are designed to convert the chemical energy stored in fuel into mechanical energy that powers the vehicle.
The materials used in the construction of these parts play a crucial role in their durability, efficiency, and performance.
Pistons
- Function:Pistons move up and down within the engine’s cylinders, compressing the air-fuel mixture and transmitting the force of the combustion to the crankshaft.
- Materials:Pistons are typically made of aluminum alloys, which offer a good balance of strength, lightness, and heat resistance.
Connecting Rods
- Function:Connecting rods connect the pistons to the crankshaft, transmitting the force of the combustion to the crankshaft.
- Materials:Connecting rods are typically made of forged steel, which provides high strength and durability.
Crankshaft, Partes del carro en inglés y español
- Function:The crankshaft converts the reciprocating motion of the pistons into rotary motion, which is then transmitted to the transmission and wheels.
- Materials:Crankshafts are typically made of forged steel or cast iron, which provide high strength and durability.
Camshaft
- Function:The camshaft controls the timing of the engine’s valves, opening and closing them at the appropriate times to allow for the intake and exhaust of air and fuel.
- Materials:Camshafts are typically made of steel or cast iron, which provide high strength and durability.
Valves
- Function:Valves control the flow of air and fuel into and out of the engine’s cylinders.
- Materials:Valves are typically made of steel or titanium, which provide high strength and durability at high temperatures.
Partes del Sistema de Transmisión

El sistema de transmisión es el conjunto de componentes que transmiten la potencia del motor a las ruedas. Está compuesto por varios elementos, cada uno con una función específica.
Componentes del Sistema de Transmisión
| Componente | Función |
|---|---|
| Embrague | Conecta y desconecta el motor de la transmisión. |
| Caja de cambios | Cambia la relación de transmisión entre el motor y las ruedas. |
| Eje de transmisión | Transmite la potencia desde la caja de cambios a las ruedas traseras (en vehículos de tracción trasera). |
| Diferencial | Permite que las ruedas giren a diferentes velocidades en las curvas. |
Tipos de Sistemas de Transmisión
Existen diferentes tipos de sistemas de transmisión, cada uno con sus ventajas y desventajas:
Transmisión Manual
- El conductor cambia de marcha manualmente.
- Ventajas: Eficiente, económico y ofrece un mayor control.
- Desventajas: Requiere más habilidad para conducir y puede ser agotador en el tráfico.
Transmisión Automática
- El vehículo cambia de marcha automáticamente.
- Ventajas: Fácil de conducir y cómoda.
- Desventajas: Menos eficiente que la transmisión manual y más costosa de reparar.
Transmisión Continua Variable (CVT)
- Utiliza una polea variable para proporcionar una relación de transmisión infinitamente variable.
- Ventajas: Muy eficiente y proporciona una conducción suave.
- Desventajas: Puede ser menos duradera que otros tipos de transmisión y más costosa de reparar.
Partes del Sistema de Suspensión

El sistema de suspensión de un automóvil es un conjunto de componentes que conectan las ruedas al chasis. Su función principal es absorber y disipar las vibraciones y los impactos causados por las irregularidades de la carretera, proporcionando así una conducción más cómoda y segura.
Los principales componentes del sistema de suspensión son:
- Muelles:Los muelles son dispositivos elásticos que absorben y almacenan energía cuando se comprimen o extienden. Los tipos más comunes de muelles utilizados en los sistemas de suspensión son los muelles helicoidales, las ballestas y las barras de torsión.
- Amortiguadores:Los amortiguadores son dispositivos hidráulicos o de gas que disipan la energía absorbida por los muelles. Controlan el movimiento de la suspensión, evitando que rebote o se balancee excesivamente.
- Brazos de control:Los brazos de control son palancas que conectan las ruedas al chasis. Mantienen las ruedas en posición y controlan su movimiento.
- Barras estabilizadoras:Las barras estabilizadoras son barras de torsión que conectan las ruedas de un mismo eje. Ayudan a reducir el balanceo de la carrocería en las curvas.
Existen diferentes tipos de sistemas de suspensión, cada uno con sus propias ventajas y desventajas. Los tipos más comunes incluyen:
- Suspensión independiente:En una suspensión independiente, cada rueda está conectada al chasis de forma independiente. Esto permite que cada rueda se mueva individualmente, lo que mejora la comodidad de conducción y el manejo.
- Suspensión dependiente:En una suspensión dependiente, las ruedas de un mismo eje están conectadas entre sí. Esto reduce los costos de fabricación, pero puede comprometer la comodidad de conducción y el manejo.
- Suspensión neumática:La suspensión neumática utiliza bolsas de aire en lugar de muelles para soportar el peso del vehículo. Proporciona una conducción muy cómoda, pero puede ser más costosa de mantener.
La elección del tipo de sistema de suspensión depende de factores como el tipo de vehículo, el uso previsto y las preferencias del conductor. Los sistemas de suspensión independientes suelen ofrecer la mejor comodidad de conducción y manejo, mientras que los sistemas de suspensión dependientes son más económicos.
Los sistemas de suspensión neumática proporcionan la conducción más cómoda, pero son más caros de mantener.
Partes del Sistema de Frenos: Partes Del Carro En Inglés Y Español
El sistema de frenos es un componente crucial de un vehículo que permite a los conductores detener o reducir la velocidad del vehículo de manera segura y controlada. Está compuesto por varios componentes que trabajan juntos para generar la fricción necesaria para detener las ruedas.Los
sistemas de frenos se clasifican en dos tipos principales: frenos de tambor y frenos de disco. Los frenos de tambor utilizan zapatas de freno que presionan contra el interior de un tambor giratorio, mientras que los frenos de disco utilizan pinzas que aprietan discos de freno montados en las ruedas.
Los frenos de disco son generalmente más efectivos y duraderos que los frenos de tambor.
Componentes del Sistema de Frenos
La siguiente tabla enumera los componentes clave de un sistema de frenos y sus funciones:
| Componente en Inglés | Componente en Español | Función |
|---|---|---|
| Brake pedal | Pedal de freno | Activa el sistema de frenos cuando se pisa. |
| Master cylinder | Cilindro maestro | Convierte la fuerza mecánica del pedal de freno en presión hidráulica. |
| Brake lines | Tuberías de freno | Transportan líquido de frenos desde el cilindro maestro a las ruedas. |
| Brake calipers (disc brakes) | Pinzas de freno (frenos de disco) | Aprietan las pastillas de freno contra los discos de freno para generar fricción. |
| Brake shoes (drum brakes) | Zapatas de freno (frenos de tambor) | Presionan contra el interior del tambor de freno para generar fricción. |
| Brake pads | Pastillas de freno | Materiales de fricción que se presionan contra los discos o tambores de freno. |
| Brake rotors (disc brakes) | Discos de freno (frenos de disco) | Discos giratorios contra los que se presionan las pastillas de freno. |
| Brake drums (drum brakes) | Tambores de freno (frenos de tambor) | Cilindros giratorios contra los que se presionan las zapatas de freno. |
Common Queries
What are the main external parts of a car?
The main external parts of a car include the body panels, windows, doors, hood, trunk, bumpers, and lights.
What are the key components of a car engine?
The key components of a car engine include the cylinder block, cylinder head, pistons, crankshaft, camshaft, valves, and timing belt or chain.
How does a car’s transmission system work?
A car’s transmission system consists of a gearbox and clutch or torque converter, which work together to transfer power from the engine to the wheels.