Beer’s law lab answer key pdf – Dive into the fascinating world of Beer’s Law with our comprehensive answer key PDF. From its fundamental principles to real-world applications, this guide will illuminate your understanding of this essential spectrophotometry technique.
Whether you’re a student seeking clarity or a professional seeking to enhance your knowledge, this answer key is your ultimate companion. Prepare to unravel the mysteries of Beer’s Law and unlock the secrets of light absorption.
Beer’s Law Introduction
Beer’s Law is a fundamental concept in spectrophotometry, describing the relationship between the absorbance of light by a solution and the concentration of the absorbing substance.
In 1852, August Beer proposed that the absorbance of a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species and the path length of the light through the solution. This law was later extended by Heinrich Lambert in 1860, who determined that the absorbance is also proportional to the molar absorptivity of the absorbing species.
Assumptions and Limitations
Beer’s Law assumes that the following conditions are met:
- The absorbing species is homogeneously distributed throughout the solution.
- The incident light is monochromatic (single wavelength).
- There is no interaction between the absorbing species and the solvent or other molecules in the solution.
Deviations from these assumptions can lead to deviations from Beer’s Law, such as nonlinear relationships between absorbance and concentration, or changes in absorbance over time.
Applications of Beer’s Law
Beer’s Law has found widespread applications in various scientific fields, including chemistry, biochemistry, and environmental science.
In analytical chemistry, Beer’s Law is a fundamental tool for determining the concentration of unknown solutions. By measuring the absorbance of a solution at a specific wavelength, and comparing it to a calibration curve prepared using solutions of known concentrations, the concentration of the unknown solution can be accurately determined.
Quality Control
Beer’s Law is also used extensively in quality control to ensure the accuracy and consistency of products. For example, in the pharmaceutical industry, Beer’s Law is used to determine the concentration of active ingredients in medications, ensuring that they meet the required specifications.
Derivation of Beer’s Law Equation
Beer’s Law is a fundamental principle in analytical chemistry that describes the relationship between the absorbance of light by a substance and its concentration. The equation for Beer’s Law can be derived using the following steps:
Consider a beam of light passing through a solution of a substance. The intensity of the light, I, decreases exponentially as it passes through the solution due to absorption and scattering by the solute molecules. The decrease in intensity is proportional to the concentration of the solute, c, and the path length of the light beam, l.
Mathematical Derivation
The rate of change of light intensity with respect to the path length is given by the following differential equation:
“`dI/dl =
kIc
“`
where kis a proportionality constant called the molar absorptivity.
Solving this differential equation gives the following expression for the intensity of the light after passing through the solution:
“`I = I 0e -kcl“`
where I0is the initial intensity of the light.
The absorbance, A, of the solution is defined as the logarithm of the ratio of the initial intensity to the intensity after passing through the solution:
“`A = log(I 0/I) = kcl“`
This equation is known as Beer’s Law. It shows that the absorbance of a solution is directly proportional to the concentration of the solute and the path length of the light beam.
Experimental Procedures for Beer’s Law Analysis
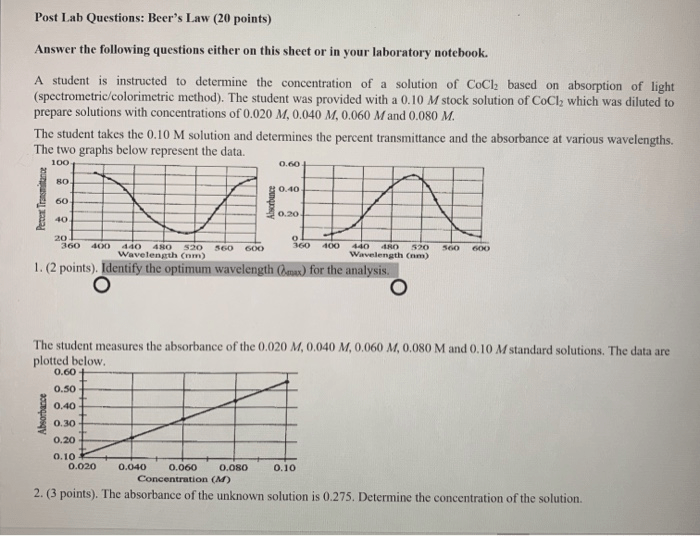
Conducting a Beer’s Law analysis involves meticulous experimental procedures to ensure accurate and reliable results. These procedures encompass sample preparation, instrument calibration, and data collection, each of which plays a crucial role in obtaining meaningful data.
Now that you’ve found the beer’s law lab answer key pdf, you might be interested to take a break and explore something different. Check out audrey flack wheel of fortune , a fascinating art piece that’s sure to captivate you.
When you’re ready to return to your studies, the beer’s law lab answer key pdf will still be waiting for you.
Sample Preparation
Sample preparation is a critical step that directly impacts the accuracy of Beer’s Law analysis. The sample must be prepared carefully to ensure its homogeneity and the absence of any interfering substances. This may involve diluting the sample, filtering it to remove particulate matter, or adjusting its pH to an appropriate range.
Instrument Calibration, Beer’s law lab answer key pdf
Prior to data collection, the spectrophotometer must be calibrated using standard solutions of known concentrations. This calibration process establishes a relationship between the absorbance and the concentration of the analyte, allowing for the accurate determination of unknown sample concentrations.
Data Collection
Data collection involves measuring the absorbance of the sample at a specific wavelength using a spectrophotometer. The absorbance value is directly proportional to the concentration of the analyte, as per Beer’s Law. Multiple measurements are typically taken and averaged to minimize experimental error.
Types of Spectrophotometers
Various types of spectrophotometers are employed in Beer’s Law experiments, each with its advantages and limitations. Some common types include:
- UV-Vis spectrophotometers: Measure absorbance in the ultraviolet and visible light range.
- Fluorescence spectrophotometers: Measure the fluorescence emitted by the sample when exposed to light.
- Atomic absorption spectrophotometers: Measure the absorption of light by atoms in the sample.
Importance of Solvents and Cuvettes
The choice of solvent and cuvette is crucial in Beer’s Law analysis. The solvent should not absorb light at the wavelength of interest and should be compatible with the sample. The cuvette should have a constant path length and be made of a material that does not interfere with the light beam.
Data Analysis and Interpretation: Beer’s Law Lab Answer Key Pdf
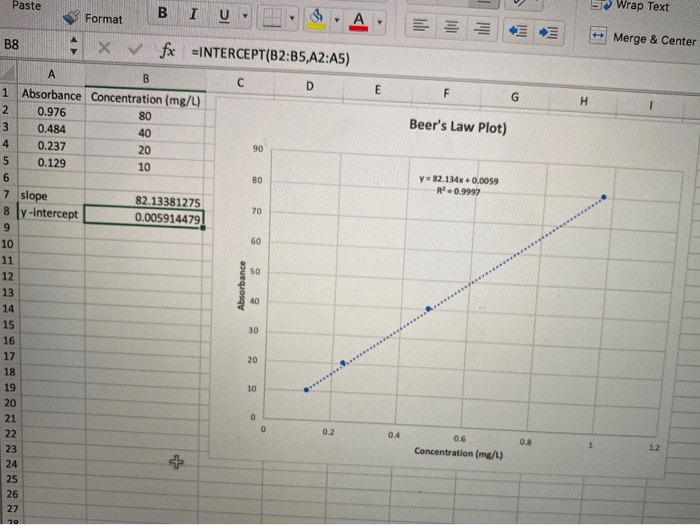
Data analysis in Beer’s Law experiments involves constructing a calibration curve and using it to determine the concentration of unknown solutions. The calibration curve is a plot of absorbance versus concentration for a series of solutions with known concentrations. The unknown concentration can be determined by measuring its absorbance and interpolating the corresponding concentration from the calibration curve.
Sources of Error in Beer’s Law Analysis
- Pipetting errors:Inaccurate pipetting can lead to errors in the concentration of the solutions.
- Spectrophotometer errors:Faulty or poorly calibrated spectrophotometers can give inaccurate absorbance readings.
- Stray light:Light from outside sources can enter the spectrophotometer and interfere with the absorbance readings.
- Temperature effects:Temperature can affect the absorbance of solutions, so it is important to keep the temperature constant during the experiment.
- Sample turbidity:Turbid samples can scatter light, which can interfere with the absorbance readings.
To minimize errors, it is important to use accurate pipettes, calibrate the spectrophotometer regularly, use a light shield to block out stray light, keep the temperature constant, and filter turbid samples before measuring their absorbance.
Applications in Real-World Scenarios

Beer’s Law is a fundamental tool in various fields, providing valuable insights into the behavior of light-absorbing substances. Its applications extend beyond the laboratory setting into real-world scenarios across industries and research disciplines.
Environmental Monitoring
Beer’s Law plays a crucial role in environmental monitoring. By measuring the absorbance of pollutants in water or air samples, scientists can determine their concentration. This information helps assess environmental pollution levels and monitor the effectiveness of remediation efforts.
Drug Analysis
In the pharmaceutical industry, Beer’s Law is employed to analyze the concentration of drugs in formulations and biological samples. This enables quality control, drug development, and therapeutic drug monitoring to ensure the safety and efficacy of medications.
Clinical Chemistry
Beer’s Law finds applications in clinical chemistry, where it is used to measure the concentration of various analytes in body fluids, such as blood, urine, and saliva. These measurements aid in diagnosing and monitoring diseases, as well as assessing the effectiveness of treatments.
Helpful Answers
What is the significance of Beer’s Law in spectrophotometry?
Beer’s Law establishes a direct relationship between the absorbance of light by a solution and its concentration. This enables us to determine the concentration of unknown solutions by measuring their absorbance.
How is Beer’s Law used in analytical chemistry?
Beer’s Law is widely used in analytical chemistry to quantify the concentration of various substances in samples. It allows for accurate and precise determination of concentrations, making it a valuable tool for quality control and research.
What are the limitations of Beer’s Law?
Beer’s Law assumes a linear relationship between absorbance and concentration. However, deviations can occur at high concentrations or in the presence of interactions between molecules.